This blog was written by Ian MacLean, a 4th Year undergraduate student at Fowler College of Business, SDSU as part of his internship program.
Artificial intelligence, or AI for short, refers to machines and their ability to exhibit intelligent behavior. This “intelligence” is achieved through the use of algorithms focused on massive sets of data. It is where we as humans apply this use of AI that we can produce results in almost any subject be it marketing, music, or in this case imagery. In these recent years, AI has seen a dramatic increase in use. It is important to realize how AI is being used and how we as consumers may benefit from this technology.
The ultimate goal of this article is to define what AI imagery is and how these tools differ, how two different AI image generators compare when using the same prompts, and how many AI images can be generated within a 1-hour timeframe.
What Is AI Imagery?
AI imagery refers to images generated by AI algorithms. These AI algorithms reference a massive dataset of images. This allows them to generate images based on specific prompting or instruction.
AI imagery can be broken down into three types of applications:
1. Image Generation: This involves using prompts for text-to-image generation.
2. Image Manipulation and Enhancement: This allows for the user to address minor imperfections like color imbalances to major more intricate modifications like cropping or touch-ups.
3. Image Understanding and Retrieval: This allows a user to give the AI tool an image and either have the AI identify and categorize the image and objects within it or have AI scrape search engines like Google for the source of the provided image.
Comparing two different AI image generation tools
Our goal was to generate images with text-to-image generation methods within AI and to evaluate and compare the outcomes from two distinct AI systems. The comparison criteria included quality in terms of fidelity and consistency, accuracy in responding to prompts, and the overall user experience. The comparison focused on two platforms: Midjourney and Lexica.
Midjourney and Lexica are AI powered image generation software that work on text-to-image prompting and both software are known for their quality in generated images. While each software is similar in product, they each have their own unique pros and cons that come with them.
To keep the comparisons as fair as possible, somewhat simple prompts were used and appropriately modified to match across each platform. Each prompt generated four images and each image shown was decided to be the single best product from each platform.
How the prompts were developed was through a simple three step AI prompting formula. It can be noted that any of these steps can be built up upon or layered in the process of writing a prompt.
Step one: Decide on a clear subject.
Step two: Include any detail or descriptions to support the subject.
Step three: Adding modifiers to the end of the prompt.
Enhancing AI Images Using Prompt Modifiers
Prompt modifiers are added at the end of prompts to further detail the image being generated. Some quick notes around the end of prompts modifiers:
- no text: No words or text in general should be used in the image generation.
- AR: The aspect ratio or resolution of the generated image. An aspect ratio of 16:9 equates to a resolution of 1920×1080.
- –V: In relation to specifically Midjourney, v followed by a number depicts the model version used to generate the image. –v 6 is the most updated version.
Testing MidJourney vs Lexica Methods
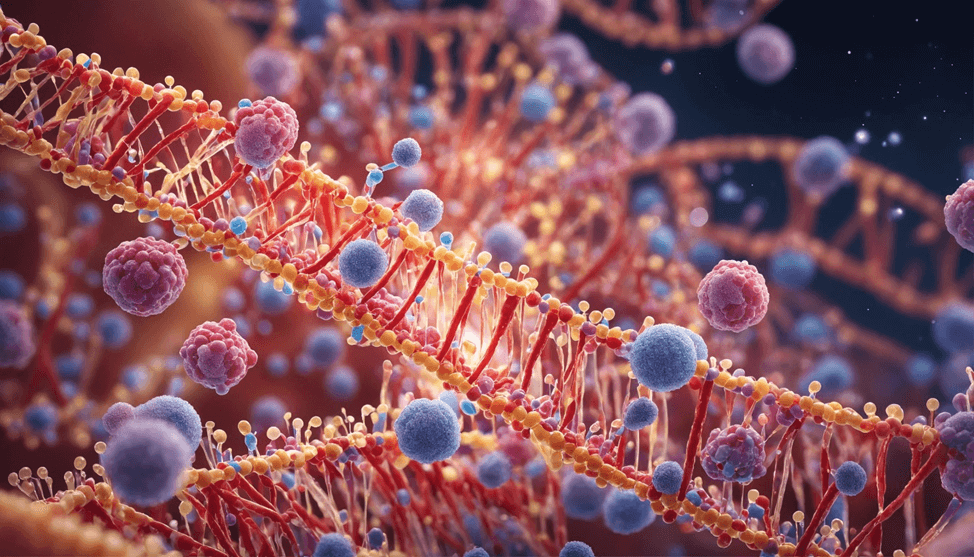
1. First, we tested the quality of output and prompt accuracy using the following prompt: “photorealistic gene therapy at the molecular level –no text
a. For Midjourney we used this prompt modifier; –ar 16:9 –v 6 – which causes the AI tool to generate images at a 16:9 aspect ratio on the newest software version available.
b. For Lexica we used this prompt modifier; –1344×768 – which forces the AI tool to generate images at an aspect ratio very close to 16:9.
1a. MidJourney result:
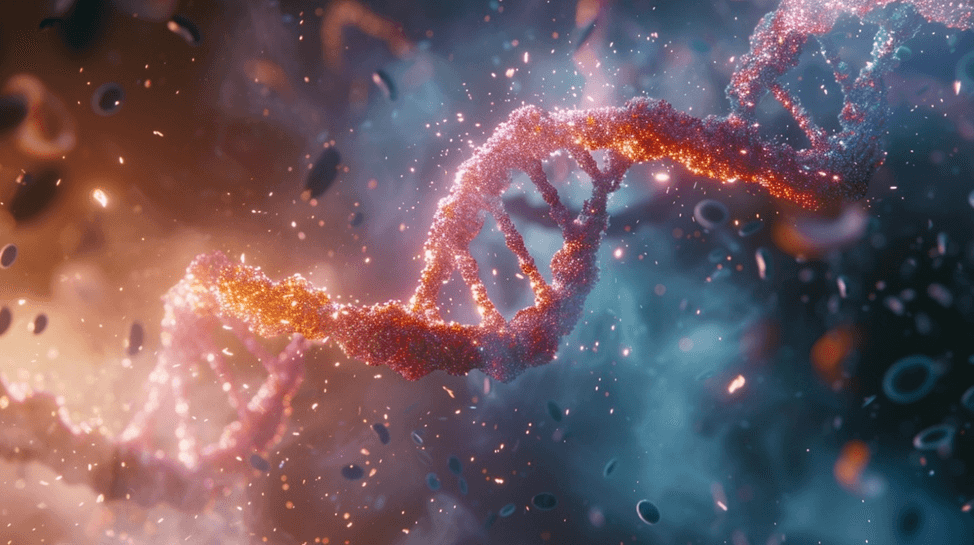
1b. Lexica result:
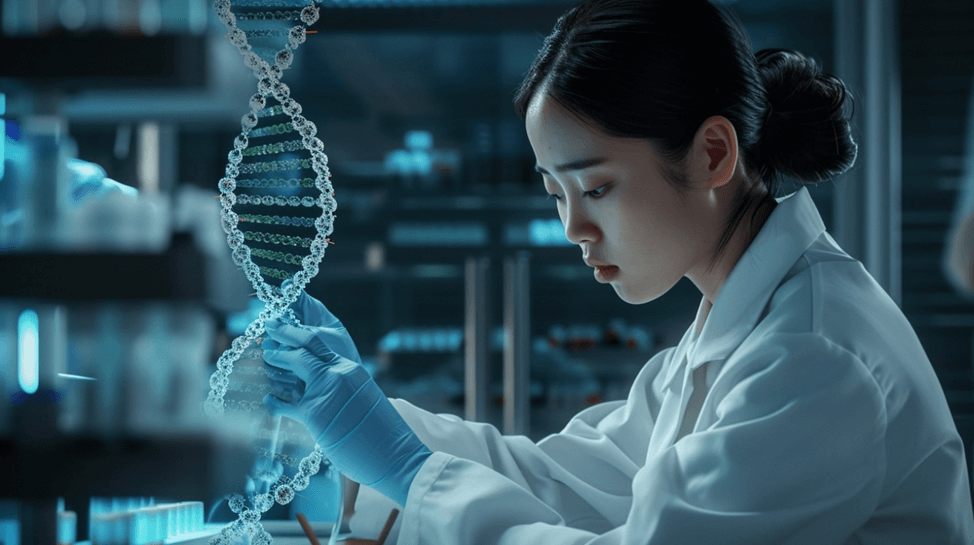
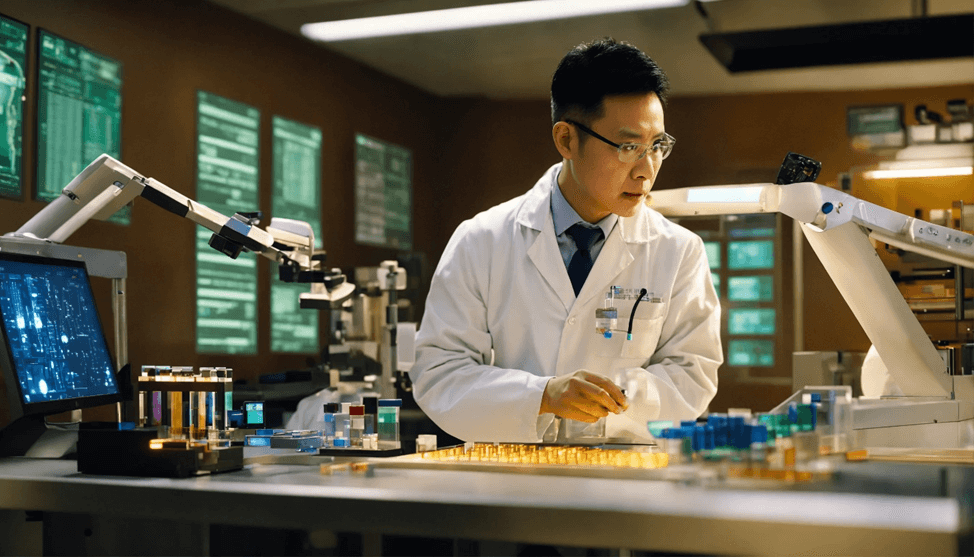
2. Second, we tested the quality of fidelity and consistency of the generated images using the following prompt: “photorealistic, asian gene therapist professional inspecting gene –no text”
a. For Midjourney we used this prompt modifier; –ar 16:9 –v 6 – which causes the AI tool to generate images at a 16:9 aspect ratio on the newest software version available.
b. For Lexica we used this prompt modifier; 1344×768 – which forces the AI tool to generate images at an aspect ratio very close to 16:9.
2a. MidJourney result:

2b. Lexica result:

Conclusion
Midjourney performed excellently with almost any prompt thrown its way. It was unparalleled with any subject except human drawings. The largest place that Midjourney failed with human subjects was the hands and faces, often having an odd amount of fingers or objects like face masks or glasses covering the whole face.
Lexica performed very well but would often stray from realism, often having more of a painting or comic feel. Most of the images that we generated with humans in a photorealistic sense would look as if they were copy-pasted from another source, resulting in very stagnant body positioning and facial emotions. The biggest bonus that came with Lexica was its consistency with human generation.
Both AI software would fail as you would add more and more people into an image. Any prompts that gave a room of more than five people would have an abnormality with at least one of the subjects.
To keep things simple, we found myself preferring Midjourney in terms of average image quality, prompt customizability, and additional features provided within the image generation process. Although Lexica’s simplicity made it easier to get started, we believe that the over simplicity results in less desirable images.
A little more on Midjourney and Lexica
Midjourney offers a user friendly experience with a comprehensive step-by-step guide available on their website, coupled with a large community on their Discord server where users may offer valuable feedback. Its main limitations stem from the necessity to prompt image generation solely through Discord, a third-party application. Additionally, they have ceased free trials, requiring users to purchase a monthly or annual subscription to begin image generation. If interested, Sciencia has a beginner friendly setup and tutorial to start your Midjourney experience.
Lexica is a very user friendly image generator that offers users 48 free image generations per week. Lexica also operates through its own web browser interface offering a more straightforward system for providing prompts. The main thing holding Lexica back is the lack of control the user has. Unlike Midjourney with its large amount of commands beyond just prompting, Lexica only features positive and negative prompting and fewer available aspect ratios.
Image Generation Sprint: Maximizing Creativity in 60 Minutes
For this test I would use Midjourney as it was both the tool I preferred using and I paid to use it so use it I shall. The goal was simply to see how many abstract tech images I could generate within 1 hour. This meant coming up with multiple prompts and expanding upon a select few of these images. I broke this test into 3 segments: the first 10 minutes for prompt research and brainstorming, the next 40 minutes for image generation, and the final 10 minutes for reviewing all the generated images to enhance or expand upon the prompt or image.
In the first 10 minutes I decided to come up with select words to throw together into a sentence for my prompt. I also decided to generate images on the latest engine Midjourney has and if colors were to be specified to be limited. The 40 minutes of image generation passed surprisingly quickly and the ability to select specific prompts or images from previous generations is built into Midjourney, so my final 10 minutes also went by very quickly.
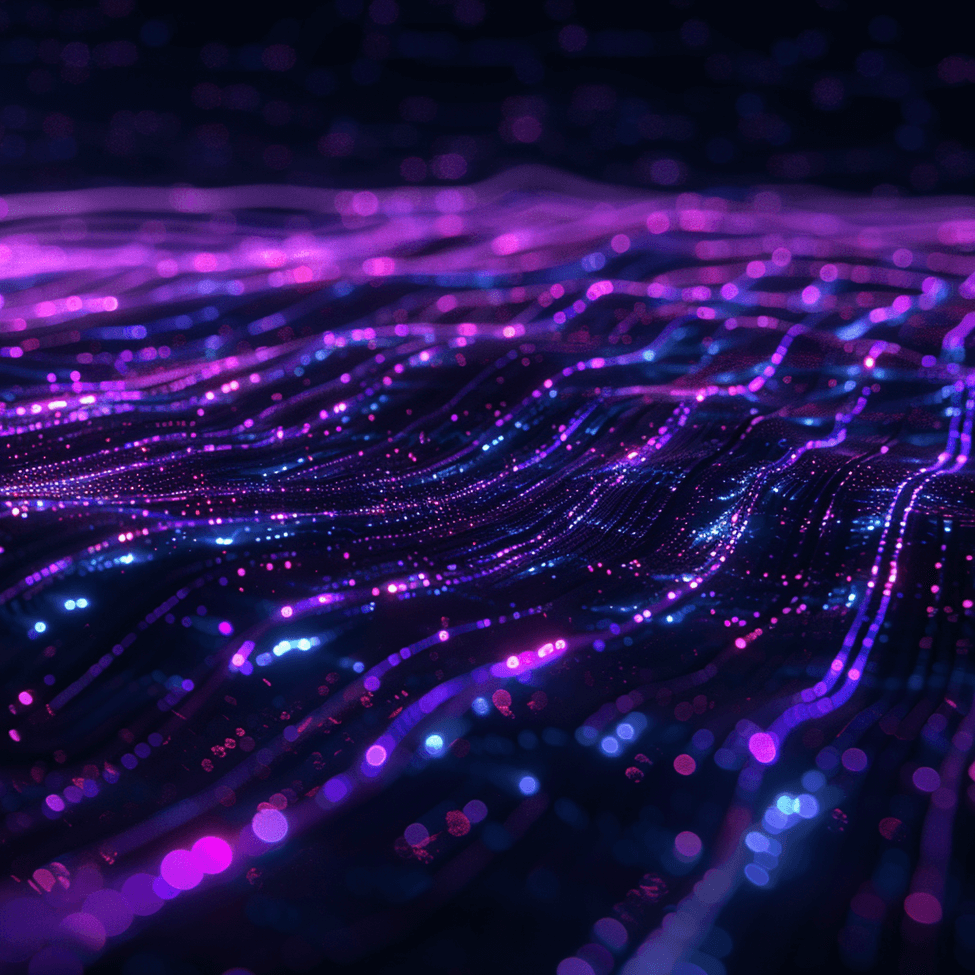
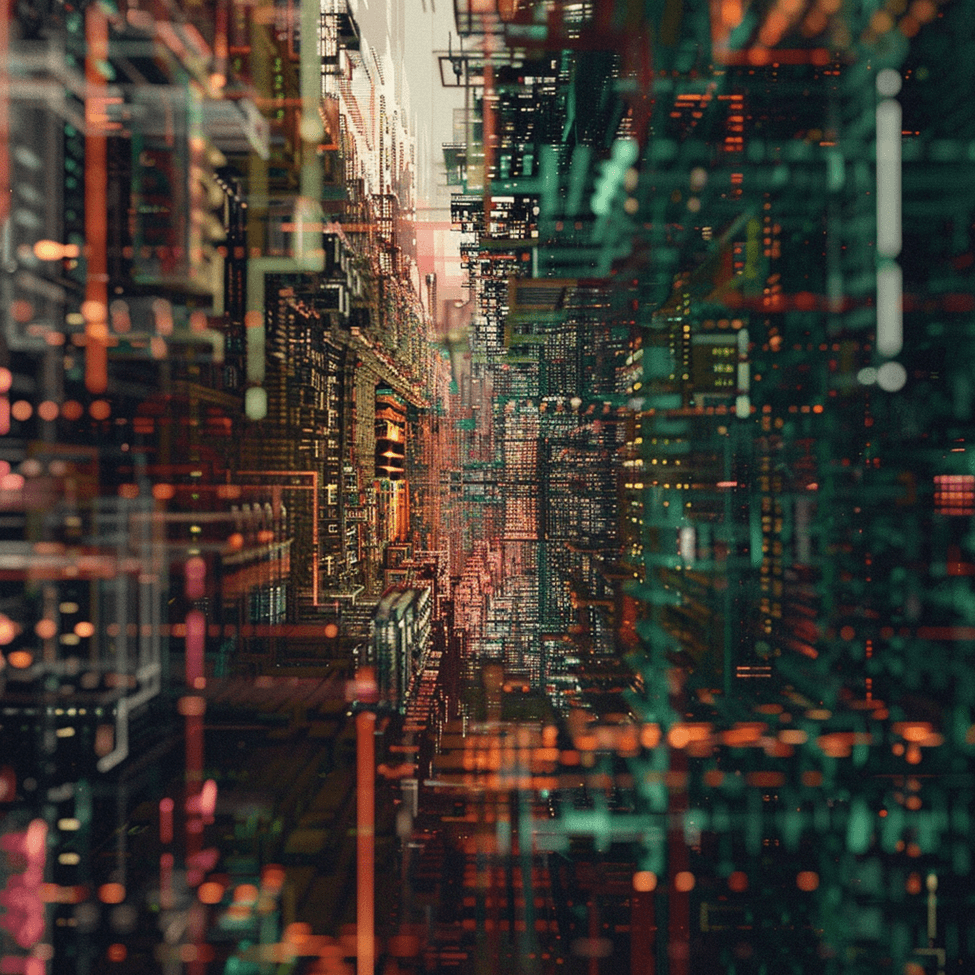
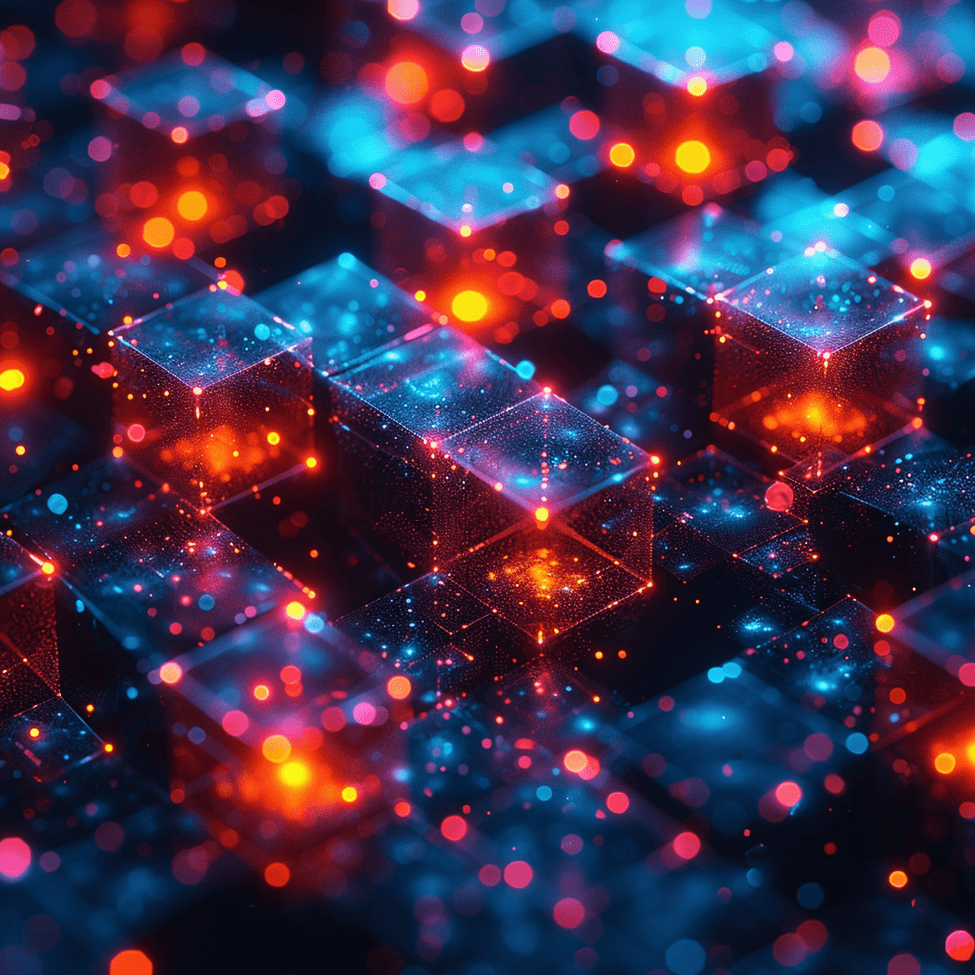
Over the hour I generated 164 images in batches of 4 equating to 41 ai generation requests made through Midjourney. Of these 164 images, 82 were downloaded for potential use. Some examples of prompts used are as follows:
- Mesmerizing visual of quantum computing, with abstract representations of qubits and entanglement emerging from the black void –v6 –stylize 500
- A whisper of bioluminescent code pulsates in the void, pulsecore, ambient, 8k, no life –v 6
- digital neural network architecture, its complexity hinted at within the void, 8k –style raw –v 6
- dark iridescent background, 8k, technologically adept, lateral movement, hex grid, warm color palette –v 6 –chaos 10
Below are a few of the resulting images generated from this hour-long test.


Adapting to AI Advancements: Embrace Awareness
After addressing AI and its significance in imagery, comparing two AI imagery tools, and performing an hour long image generation test, we can conclude that utilizing AI as a tool for image generation is a very user friendly process. The amount of AI available to consumers is growing by the day which may result in wondering which AI tool to use. The greatest piece of advice we can give is to dive in headfirst and give AI imagery a try and use it responsibly. Do keep in mind that as AI technology is constantly improving, staying informed with its capabilities and anticipated advancements is important. Remaining open and proactive will ensure we maintain and maximize the potential of our AI usage.
AI Disclosure Statement: Some of this text content was generated with ChatGPT and Gemini and the images were made on Midjourney and Lexica.



